Health Tips
Condom Myths

Studies show condoms are 80% to 97% effective in preventing HIV transmission if they are used correctly every time you have sex.
Condoms break a lot:
Less than 2% of condoms break when they are used correctly: no oils with latex condoms, no double condoms, no outdated condoms.
HIV can get through condoms:
HIV cannot get through latex or polyurethane condoms. Don’t use lambskin condoms.
When the Condom Breaks
Depending on when the condom breaks during sex, there are different courses of action you can take:
- If your partner has not yet ejaculated, he should quickly pull out, take off the damaged condom and put on a new one.
- If the breakage is discovered after ejaculation, you can insert two applications of spermicide into your vagina as soon as possible; both partners should wash with soap and water to get rid of any semen that may have leaked out. However, it is important to note that this is not a very effective method of emergency contraception and is in fact one of the least reliable ways to prevent pregnancy. Women should not douche.
- Contact your health care provider or pregnancy resource center as soon as possible to discuss STD tests, pregnancy testing, and other options that may be available to you.
Remember to always store your condoms away from sunlight, in a cool, dry place. Also, check the expiration date on your condom package and never use a condom that has expired. If you cannot find an expiration date (usually marked as “Exp”), then check for the date of manufacture (usually marked as “MFG”). Do not use any condoms five years after the date of manufacture. If your condoms contain spermicide, then throw them out two years after the date of manufacture.
Taking the Condom Off
Condoms should be removed shortly after sex, before a man has lost his erection. To remove a condom:
- Your partner should hold onto the base of the condom as he pulls out. This will help prevent the semen from leaking out
- Inspect the condom for any signs of breakage or leaking.
- Pull the condom off and throw the used condom in the garbage
Using a Condom

- Carefully tear open the wrapper. If you are using lubricant, place a drop or two inside the condom.
- If your partner has not been circumcised, then pull back the foreskin.
- Leaving a ½ inch of space at the top, pinch the tip of the condom and begin to roll it on to the penis.
- The roll should lie on the outside of the condom. Unroll the condom all the way to the base of the penis.
- Make sure there are no air bubbles as these can cause the condom to break during sex.
- If you like, you can also put some more lubricant onto the outside of the condom once your partner has it on.
While there are many safe lubricants you can use with condoms, others can damage or weaken the condom, especially latex condoms.
Before Sex

Some couples find that sex is more enjoyable and comfortable if a lubricant is used. While there are many different types of lubricants available, and many other substances that you can use as a lubricant, it is important to remember that any lubricant that is oil-based can weaken a latex condom. Therefore, look for lubricants that are water-based.
If you are having sex for the first time with a new partner, be sure to discuss the use of condoms with your partner before you have sex.
How do you dispose of a used condom?
All used condoms should be wrapped in tissue or toilet paper and thrown in the bin. Condoms should not be flushed down the toilet as they may cause blockages in the sewage system.
Latex condoms are made mainly from latex with added stabilizers, preservatives and vulcanizing (hardening) agents. Latex is a natural substance made from rubber trees, but because of the added ingredients most latex condoms are not biodegradable. Polyurethane condoms are made from plastic and are not biodegradable.
What do you do if the condom won’t unroll?
The condom should unroll smoothly and easily from the rim on the outside.
If you have to struggle or if it takes more than a few seconds, it probably means you are trying to put the condom on upside down. To take off the condom, don’t try to roll it back up. Hold it near the rim and slide it off. Then start again with a new condom.
What do you do if the condom slips up or breaks?
Whilst you are having sex, check the condom from time to time to make sure it hasn’t split or slipped up. If it slips up, roll it back down immediately. If it comes off you will have to withdraw and put on a new one.
If a condom breaks during sexual intercourse, pull out quickly and replace the condom. If the condom has broken and you feel that semen has come out of the condom during sex, you should consider emergency contraception such as the morning after pill.
What are the other reasons to use a condom?

- Have none of the medical side-effects that some other birth control methods may have.
- Are available in various shapes, colours, flavours, textures and sizes. These can all increase the fun of having sex with condoms.
- Are widely available in pharmacies, supermarkets and convenience stores. You don’t need to visit a doctor or have a prescription.
- Make sex less messy.
- Are user friendly. With a little practice, they can also add confidence to the enjoyment of sex.
Is using a condom effective?
If used properly, a condom is very effective at reducing the risk of HIV infection during sexual intercourse. Using a condom also provides protection against other sexually transmitted diseases, and protection against pregnancy. In the laboratory, latex condoms are very effective at blocking transmission of HIV because the pores in latex condoms are too small to allow the virus to pass through.
However, outside of the laboratory condoms are less effective because people do not always use condoms properly.
TAKE TIME AND CARE TO READ AND FULLY UNDERSTAND THE CORRECT USE OF CONDOMS BEFORE SEX
By understanding how to use a condom properly, you and your partner will be able to enjoy an intimate experience without any worries or concerns.
NB. Handle with care. Condoms can be torn by fingernails and sharp objects such as jewellery and body piercings.
NEVER USE A CONDOM MORE THAN ONCE
Latex: only water soluble or silicone based lubricants should be used with latex condoms. Do not use oil-based lubricants such as petroleum jelly or oil-based pessaries as these can damage latex condoms. Unity condoms are dermatologically tested. However, some individuals may experience sensitivity to latex. If you have any concerns or may be sensitive or allergic to latex, consult a doctor before use. Some topical medicines applied to the penis or vagina can damage latex. Ask your pharmacist or doctor before use.
Usage: check the expiry date on the foil before use. If used properly, latex condoms will help to reduce the risk of transmission of HIV infection (AIDS) and many other STis. Non-vaginal use of condoms may increase the risk of them slipping or being damaged.
No method of contraception can provide 100% protection against pregnancy or the transmission of HIV and STis. If, after intercourse, you are concerned for whatever reason that you or your partner may have become pregnant, contact your doctor immediately.
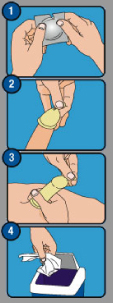 INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Either partner can put the condom on the erect penis during foreplay. Care should be taken to do this to help prevent pregnancy and/or transmission of STis. The foil should be opened at the jagged edge and the condom taken out with care.
2. Check the roll is on the outside, otherwise the condom is inside out. Gently squeeze the teat to prevent trapped air.
3. The condom can then be put on and rolled down. If it rolls back up during sex, it should be rolled back down straight away. If the condom comes off, use a new one.
4. After climaxing, (while still erect), the condom should be held In place at the base of the penis before withdrawal. It can then be wrapped in a tissue and put in the bin. Do not flush down the toilet.
